Condition Contract Management in SAP S4 hana: Simplifying Settlement Management
This blog explains the essential configuration steps for Condition Contract Management, a business process used to manage conditions with suppliers and customers, particularly those requiring subsequent settlement. The solution comprises the administration of conditions in condition contracts together with agreements about the relevant business volume and the settlement of condition contract in order to create corresponding amounts receivable and payable in Financial accounting.
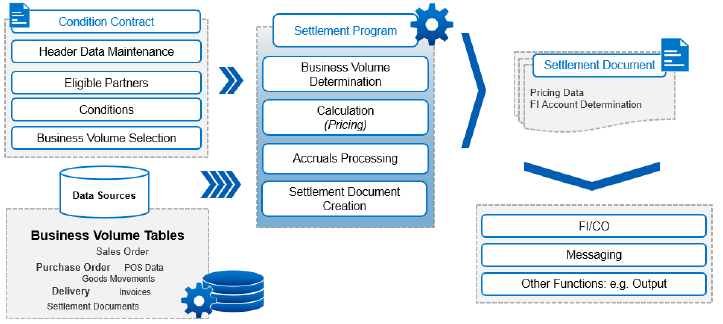
Introduction of Condition Contract Management (CCM)
Condition Contract Management in SAP is a crucial business process for managing conditions with suppliers and customers, particularly those requiring subsequent settlement. This system allows for the administration of conditions in contracts, agreements on business volume, and settlement processes, leading to corresponding amounts receivable and payable in Financial Accounting. The main elements for which the configuration must be specified include settings for the condition contract processing and settlement, as well as settings for the settlement documents which the system creates in a condition contract settlement. The central configuration parameter is the condition contract type, which contains settings both for the condition contract processing and settlement.

Understanding Condition Contract Management:
CCM is a system that manages the settlement amount during the settlement process. It involves three main steps: Configuring Condition Contract Conditions, Configuring Condition Contract Maintenance, and Configuring Condition Contract Settlement. The first step involves defining pricing conditions for the settlement amount, including rebate and accrual conditions. The second step involves defining parameters for conditional contract types and their respective parameters. The third step involves enhancing existing condition contract types with these parameters. The configuration process follows the usual pricing procedure for sales orders.
For both purchase-sided and sales-sided conditions contracts, the configuration settings are similar. To make the required customizing settings, choose Logistics—General Settlement Management. To define condition tables, define Basic Settings Pricing Maintain Condition Table. For purchase-sided conditions, define Basic Settings Pricing Materials Management (MM) Define Access Sequences. For suppliers, define Customizing activity Condition Contract and Conditions Purchasing. To define purchasing conditions and activate them for CCM, choose Customizing activity Define Condition Types.
Configuration Steps :Condition Contract Management in SAP S4 hana
Configure Condition Contract Conditions
Customizing settings necessary for defining and controlling pricing conditions relevant for calculating the settlement amount during the condition contract settlement in CCM. The configuration of contract conditions aligns with the typical configuration procedure for pricing, akin to that for sales orders. The Customizing for Settlement Management encompasses corresponding activities to streamline the configuration task for this solution.
Settings for Purchase-Sided and Sales-Sided Condition Contracts

Define Condition Tables
To define condition tables utilized for condition types in CCM, access the Customizing activity Basic Settings ->Pricing Maintain Condition Table.
- The condition table typically features the condition contract number as the key field. This field is denoted as “Condition Contract” in the configuration screen, with the technical field name being COCO_NUM.
- SAP offers examples of condition tables such as 4AB Number and 163 Number/Material in the standard delivery. The former has the condition contract number as the sole business data-related key field, while the latter includes both the condition contract number and material as key fields.
- Extending the field catalog for table key fields is required if additional key fields are necessary for condition tables. This can be achieved through the Customizing activity Basic Settings-> Pricing Extend Field Catalog for Condition Tables.
Define Access Sequences
To define access sequences for condition types associated with purchase-sided condition contracts in C, access the Customizing activity Basic Settings ->Pricing-> Materials Management (MM) Define Access Sequences. Ensure the specification of (blank) Access sequence relevant for pricing as access category. SAP provides the access sequence COMP CCM: Only Condition Contract in the standard delivery, containing accesses to condition tables 163 Number/Material and 4AB Number.
Condition Contracts for Suppliers
To configure contract conditions related to condition contracts with a supplier as the contract partner, access the Customizing activity Condition Contract Management ->Conditions Purchasing.
Define Purchasing Conditions and Activate Them for Condition Contract Management
To define condition types related to purchase-sided condition contracts, access the Customizing activity Define Condition Types. SAP offers exemplary condition types like REBT Rebate and REBA Bonus Accrual in the standard delivery.
Defining Purchasing Condition Type Groups with Purchasing Conditions
For the utilization of condition types in condition contract maintenance, it’s necessary to group purchasing condition types in purchasing condition type groups. These conditional then assigned to a condition contract type.
Conditional Contracts for Customers
To configure contract conditions related to condition contracts with a customer as the contract partner, access the Customizing activity Condition Contract Management ->Conditions Sales.
Define Sales Conditions and Activate Them for Condition Contract Management
To define condition types related to sales-sided condition contracts, access the Customizing activity Define Condition Types.
Defining Sales Condition Type Groups with Sales Conditions
Similar to purchasing conditions, for the usage of sales condition types in condition contract maintenance, it’s essential to group sales condition types in sales condition type groups. These groups are then assigned to a condition contract type.
Other Conditions
Configuration for other required condition types follows the same pattern as described above for contract conditions. Key activities include:
- Defining condition tables
- Defining access sequences
- Defining condition types
Parameters include condition class B Prices, calculation type B Fixed amount, and condition category H Basic price.
- Settled Rebate: A manual condition type that adopts the calculated business volume amount from previous settlement runs. Parameters include condition class A Discount or surcharge, calculation type B Fixed amount, and an initial condition category.
- Settled Accruals: A manual condition type that adopts the determined amount for the accruals reversal within settlement runs. Parameters include condition class A Discount or surcharge, calculation type B Fixed amount, and an initial condition category.
Configure Condition Contract Maintenance
This document provides guidance on the Customizing settings required for processing condition contracts in Condition Contract Management. Before proceeding with the configuration, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Purchasing condition type groups and/or sales condition type groups have been created, as described in the “Configuring Condition Contract Conditions” Implementation of ABAP classes intended for additional checks.
The configuration for condition contract maintenance involves two main steps: defining and configuring parameters for condition contract types, followed by defining the condition contract types themselves.

Define and Configure Parameters for Condition Contract Types
- Define Number Ranges: Set up number ranges for condition contract types via Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define Number Ranges.
- Defining Condition Contract Categories: Optionally, group condition contract types using condition contract categories. conditional activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define Condition Contract Categories.
- Define and Configure Field Status Groups: Optionally, utilize field status groups to manage condition contract header fields. Define these groups via Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define Field Status Groups for Header Fields.
- Define and Configure Status Profiles: Optionally, set up status profiles for custom status management of condition contracts. Access Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define and Configure Status Profiles.
- Define and Configure Critical Changes: Optionally, define critical changes groups containing critical changes for condition contracts. Access Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define and Configure Critical Changes Groups.
- Define and Configure Action Profiles: Optionally, utilize action profiles to define actions for the Post Processing Framework. Access Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define and Configure Action Profiles.
Define and Configure Condition Contract Types
- Defining Condition Contract Types: Define condition contract types with specified parameters. Access Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Define Condition Contract Types. Note:
- Specify the Type of Contract Partner (supplier or customer).
- Specify the Type of Eligible Partners if applicable.
- Enter values for configured parameters.
- Make further settings to determine layout and processing behavior.
- Activate Additional Functions for Condition Contract Maintenance: Optionally, activate additional functions for condition contract maintenance. Access Customizing activity Condition Contract Management Condition Contract Activate Additional Functions for Condition Contract Maintenance.
- Special Condition Contract Types: Customer, Supplier, and Plant Lists: Configure special condition contract types to function as customer, supplier, or plant lists. Utilize the “No Contract Partner” option for the Type of Contract Partner attribute, and specify the Type of Eligible Partners accordingly.
Standard Configuration for Restrictions and Checks
The condition contract maintenance employs a standard configuration for restrictions and checks, utilizing ABAP classes. It involves:
- Defining restrictions and checks using ABAP classes.
- Assigning ABAP classes to table structures and corresponding fields.
- Assigning ABAP classes to field chains.
- Configuring check categories to control the usage of ABAP classes based on condition contract scenarios.
Enhancements Using Business Add-Ins
SAP provides Business Add-Ins (BAdIs) to enhance the user interface and processing behavior of condition contracts. Access Customizing for Condition Contract Management via the activity Enhancements Using Business Add-Ins Condition Contract Maintenance.
Configure Condition Contract Settlement
Condition contract the Customizing settings required for processing condition contract settlement. In the settlement process, the settlement amount is determined for relevant business partners over a certain period based on business volume .Before configuring the condition contract settlement, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Create a database view in the data dictionary required for selecting business volume data.
- Configure settlement documents in the Customizing for Settlement Management.
- Create factory calendars to be used as settlement calendars.
The configuration for condition contract settlement involves five main areas:
- Business volume determination
- Settlement calendar
- Calculation of the settlement amount
- Creation of settlement documents
- Reversal of accruals

Configure Business Volume Determination
The business volume serves as the basis for condition contract settlement. Typically, it represents a certain amount derived from business transactions with a partner. Optionally, it can be differentiated based on parameters influencing the settlement amount, such as merchandise categories or quantities.
- Define and Configure Profiles for Business Volume Determination: Specify the data source and information to be selected. Use Customizing activity Define and Configure Profiles for Business Volume Determination.
- Define and Configure Field Combinations and Sets of Field Combinations: Define selection criteria for business volume selection. Use activities Define Field Combinations for Business Volume Selection and Define Sets of Field Combinations.
- Assign Profiles and Sets of Field Combinations to Condition Contract Types: Specify the condition contract settlement type and assign the profile and set of field combinations. Use activity Specify Settlement Settings for Condition Contract Types.
Extended Configuration with Several Data Sources
Config condition usiness vomanagementmination to involve multiple data sources for flexibility.
- Define Business Volume Table Groups: Specify sets of business volume tables. Use activity Define Business Volume Table Groups.
- Specify Business Volume Table Groups in Profiles: Assign additional business volume tables and relevant groups. Use activity Define and Configure Profiles for Business Volume Determination.
- Define Selection Groups: Specify groups for selection criteria. Use activity Define Selection Groups.
- Configure Selection Groups in Profiles: Assign relevant selection groups to profiles. Use activity Define and Configure Profiles for Business Volume Determination.
In summary, Condition Contract Management is a system that manages the settlement amount during the settlement process. It includes configuration settings for both purchase-sided and sales-sided conditions contracts. SAP provides exemplary condition types for settlement amount calculation and posting accruals, with the Accruals checkbox in the Control data 2 group box selected. Customizing settings for other conditions are also available, and the system ensures efficient and accurate settlement processes.
You might also like the below articles.
- Comprehensive guide to go live
- SAP EHS Module
- Power of generative ai in sap
- SAP Joule Comprehensive Guide
- Mastering the dunning process sap
- Creation of chart of accounts in sap fico
- Different roles of an sap consultant
- understanding sap system landscape
- Product costing in sap
- Copa in sap
- subcontracting process in sap mm
- SAP S4hana cloud
- Disaster Recovery in SAP HANA Cloud
- SAP ABAP beginner’s journey
- Year-end activities in sap
- SAP Project system module
- SAP DMS
- SAP ECC vs SAP HANA
- SAP Qualtrics
- Advance ATP
- SAP Project Implementation
- Exploring sap competitors
- Procure to pay process
- Order to cash process
- SAP S4hana inventory management
- SAP CPQ
- S4hana cloud upgrade schedule
- SAP Lumira
- SAP Signavio
- OpenText vim
- SAP Commerce cloud
- SAP S/4HANA Data migration tools
- SAP CPI integration
- SAP GTS for International Businesses
- Rise with sap
- What is Hyperscalers
- SAP bpc comprehensive guide
- SAP Business One
- Production Planning