Resource Scheduling for Maintenance Planner Fiori App - Complete Functionality


In this article, we’ll explore different ways to implement checklists in SAP PM/EAM, using our favorite example: the Texas Workshop. But remember, here I just show a portion of it—the video covers everything in detail, so make sure to check it out!
Imagine a technician, Pasha Dankov, receives a maintenance order for a vehicle. The checklist includes:
Currently, Pasha uses a paper-based checklist, manually ticking off tasks and writing notes. But wouldn’t it be better if SAP handled all of this? That’s why, we will explore five different ways to digitize checklists in SAP!

PM Task Lists are predefined sets of maintenance steps that can be reused across multiple maintenance plans and work orders. They help standardize procedures and ensure technicians follow a structured workflow. Technically, it is possible to reflect a PM checklist as a Tasklist, with multiple operations inside. Following our example – each type activity like general inspection, checking fluids and levels etc. could be a separate operation with detailed description (called long text in SAP) inside. And this description could hold information about the checks, just have a look:

Pros:
Cons:
How it works:

Using SAP’s Document Management System (DMS), checklists can be stored as PDF attachments and linked to maintenance orders or task lists. However, this is not a real paperless approach. You still stick to the paper document in a .PDF form for example, which most probably needs to be anyway printed, filled out, scanned and uploaded again. Or, if you are equipped with a .PDF reader on your mobile device, it’s possible to capture the data and upload straight away, from the device.

Pros:
Cons:
Measuring Points in SAP allow users to record qualitative and quantitative maintenance data. They are linked to specific equipment or functional locations and enable structured condition-based monitoring.

Pros:
Cons:
For companies requiring a tailored solution, custom-developed checklists offer flexibility. By creating custom SAP tables and UI enhancements, organizations can streamline their maintenance processes and enhance reporting.

Pros:
Cons:
SAP Inspection Checklists integrate Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) with Quality Management (QM) to provide a structured approach to inspections. This solution is beneficial for industries requiring compliance and regulatory adherence. Important thing – this feature is available from S/4HANA 2021 onwards.

Pros:
Cons:
This is a new product and new approach how to handle the checklists. BTP forms can be easily build via drag-and-drop activity. You are equipped with a form builder, the form which you build can be then embedded in the standard Fiori Application ‘Create Maintenance Request’ or ‘Perform Maintenance Jobs’. If you have a custom mobile application – you can also embed it there. And if you plan to use SSAM – SAP Service and Asset Manager, this feature is already there, by standard. Of course Dynamic Form requires separate license, as this is another product in your environment.

Pros:
Cons:
Checklists are a fundamental part of SAP PM/EAM, and now you know multiple ways to implement them. Whether you’re going for a simple task list or an advanced digital solution, choosing the right approach depends on your industry, processes, and system capabilities.
And remember—this is just a portion of what I covered in the below video.
Cheers,
Dan
The post 5 Ways to Implement PM Checklists in SAP S/4HANA EAM appeared first on SAP dude.
Definition: Equipment Bill of material in SAP PM Module is a part of Master Data in SAP PM Module. It is used to capture the information about the spare parts of a particular technical object (Equipment). This information is used during maintenance processing which helps the maintenance planner to search the relevant spare part to replace. Planner is not required to search the spare part into complete material master in maintenance order.
As a consultant it is always recommended to create Equipment Bill of material.
How to create an Equipment Bill of Material in SAP PM:
Step 1: Run t Code IB01 or else follow this path on the SAP easy access screen:
SAP Menu -> Logistics -> Plant Maintenance -> Management of Technical Objects -> Bill of Material -> Equipment BOM -> IB01 – Create
Step 2: Create Equipment BOM initial screen will appear. Here you must enter the equipment with reference to which you want to create the bill of material.
Step 3: Select the plant to which equipment belongs to or where equipment is physically installed.
Step 4: Select the BOM usage 4 – Plant Maintenance. Here you will get total 8 entries because bill of material is used in other modules also .Like Production Planning, Material Management, Sales Distribution. You will be able to use this Equipment BOM in maintenance processing only if you select BOM usage as 4.
Step 5: Press enter to continue. Now the general item overview screen will appear.
Step 6: Here you can assign all the spare parts of the equipment with quantity.
Step 7: In the material tab. Select the desired material and enter the quantity.
Step 8: Select the item category very carefully. There are two item categories are applicable here. L and N. L means Stock item, which in turn means that material is always available in warehouse for use. In the maintenance order a reservation will be created for this material.
However, N means that material non stock material, which means that a purchase requisition will be triggered from the maintenance order if this material required for maintenance.
Step 9: Afterwards click on SAVE button. Once it is saved. It is ready for use in maintenance order.
Application: It is frequently asked in the interview question that what is the use of Equipment Bill of material. Here is the answer: Whenever you create any maintenance order with reference to this equipment, then in the component tab, every maintenance planner wants to have the list of spare parts related to that particular equipment for which maintenance order is created, not the entire material master, where you have thousands of materials.
Here business user should go to the top menu bar click on the Extras -> Reference Objects -> Structure List. This will open the same material list which you have created in IB01 t code. Other than menu bar you may also click on a LIST button with a flower on it. This will do the same.
The post Equipment Bill of Material appeared first on VaibhavERP.
In my previous posts I have explained task list in sap pm and equipment task list. Now I will share knowledge on Functional Location Task List in SAP PM. Functional Location task list is not widely used in SAP PM Module. However, as a consultant you must share the knowledge about it with client.
Functional Location Task List is an Object based task list. We call it object based because it is created with reference to a Functional Location (Object). In SAP we use indicator ‘T‘ to identify functional location task list. T code to create a Functional Location task list is IA11.

Functional Location Task List can be used in the preventive maintenance and routine maintenance of functional locations in plant area. It is used where some special maintenance operations are required to be performed at scheduled intervals. Suppose a maintenance work is to be performed on a functional location and maintenance tasks are specific (not general) to that area. In such a situation, we use functional location task list.
The concept and working of functional location task list is exactly same as equipment task list. Therefore, I request you to refer equipment task list also.
Step 1: Run t code IA11 or go to node on SAP Easy Access Screen as shown in the below screen shot.


Step 2: Enter functional location id and press enter or click on tick mark as shown in below screen shot.

Step 3: Planning Plant and Main Work Center will automatically copied from Functional Location Master Data. Group Counter will automatically update from system. Group is also updated internally from system. Here you must selected Usage = ‘4’ – Plant maintenance as shown in below screen shot.
Step 4: Select Planner group from drop down.
Step 5: Select Status = ‘4’ – Release (general)
Step 6: Select System Condition. It shows the state of functional location during maintenance. Whether functional location will be in operation or not in operation when these maintenance operations will be performed.

Step 7: Maintenance Strategy decides the cycle (frequency) of each maintenance operation. You can keep this field blank (for Single Cycle Plan) or select the maintenance strategy from drop down. Maintenance strategy is defined in t code IP11.
Step 8: Click on Operation Button at the top as shown in the below screen shot.

Step 9: See the below screen very carefully. It has very important information.

Main Work Center is copied from Task List header. Here you can see that it is maintained for each maintenance operation because it tells us who will execute the particular maintenance operation.
Control Key decides whether operation will be executed internally or externally. Means if an operation is executed by our own man power then we will select control key as PM01. However, if we want an external person or contractor to do the operation then we select control key as PM03.
Operation description give us clear cut information and sequence of maintenance activities to be performed on technical object.
‘Work’ (Man hours) is calculated as per formula :
Work = No. of persons X duration
No. of persons means the count of persons who are deployed to execute the maintenance operations.
Duration is the time taken by maintenance person to finish the task.
Calculation Key is the indicator which decides the formula to calculate Work. Sometimes client does not want to calculate man hours. They only want to calculate duration, then they select calculation key = ‘1’. But generally we recommend to calculate man hours using Calculation Key = ‘2’.
Activity Type is a very important function. It is copied automatically from Main Work Center data. It is defined by Controlling person. It contains the information of rate of man hours. When it is multiplied with Work (man hours), it give the cost of internal services. This helps in maintenance order costing. Do not confuse Activity type with Maintenance Activity Type. Both are entirely different.
Integration : Assignment of Activity Type in Task List and Maintenance order is an integration of PM module with CO module. CO person creates Activity type using t code KP26. Even a PM consultant can easily learn step by step process of creating Activity Type. I will include a separate article on this topic in near future.
Step 11: Assign components (spare parts) to the operations wherever applicable. For example: For cleaning and lubrication maintenance person can have requirement of Lubricant or maintenance person wants to replace the bearing of a machine. To capture such information first select the operation for which you want to issue material from warehouse. Then click on Component button at bottom (as shown in below screen shot).

Step 12: A new screen will appear where we can select the material (spare part) and enter quantity. We can also select the relevant Item Category.
If item category is ‘L‘, then material will be issues from warehouse through reservation.
If item category is ‘N‘, then material will be procured through procurement cycle (PR -> PO -> GR).

Step 13: If you want to execute a certain maintenance operation by an external agency (Contractor), then you must select the control key PM03. By using control key PM03, you can assign services from service master, quantity and gross price. This helps in calculating the cost of externally procured services in maintenance order. Afterwards scroll to right side of the scren to enter some more important information.

Step 14: After scrolling to right hand side of the operation screen, you will have to maintain Cost Element, Material Group and purchase Group. All these fields are entered at operation level. Cost element is entered to determine the g/l account. Rest other two fields are related to purchase of external services.

Step 15: Afterwards click on Service Package button it will open a new screen where you can enter the service number, with quantity and gross price.
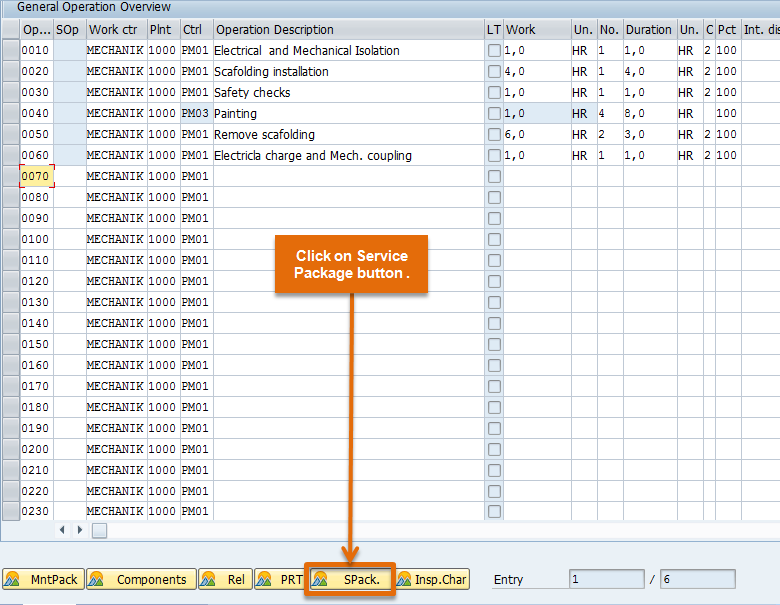

Step 16:Click on back button and press SAVE button. This will save functional location task list.
The post Functional Location Task List in SAP PM appeared first on VaibhavERP.

Task list in SAP PM is the check list which is used to do maintenance of a machine in manufacturing area.
For example: Task list to do maintenance of a pump can have following check points:

It is an object based task list. It is created with reference to a specific equipment. It is identified by the indicator ‘E‘.
It is also object based task list. It is created with reference to a specific Functional Location. It is identified by the indicator ‘T‘.
It is not an object based task list. It is general task list without reference to a specific technical object. It is identified by the indicator ‘A‘. It can be defined as per the type of asset (or machine). A name can be given to the task list which is applicable to a set of technical object.
The post Task List in SAP PM appeared first on VaibhavERP.
We have already discussed about task lists in earlier post. Now we will focus on Equipment Task List in SAP PM.
Equipment Task List is an Object based task list. We call it object based because it is created with reference to an Equipment (Object). In SAP we use indicator ‘E‘ to identify equipment task list. T code to create a Equipment task list is IA01
Equipment Task List is widely used in the preventive maintenance and routine maintenance of critical and unique equipment, which requires some special maintenance operations to be performed at scheduled intervals. Suppose a maintenance work is to be performed on an equipment and maintenance tasks are specific (not general) to that equipment. In such a situation, we use equipment task list.
Step 1: Run t code IA01 or go to node on SAP Easy Access Screen as shown in the below screen shot.

Step 2: Enter Equipment id and press enter or click on tick mark as shown in below screen shot.
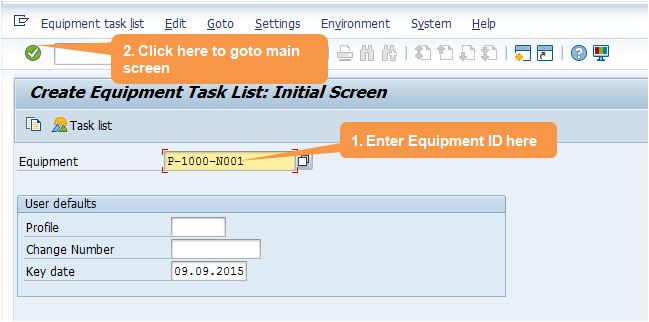
Step 3: Planning Plant and Main Work Center will automatically copied from Equipment Master Data. Group Counter will automatically update from system. Group is also updated internally from system. Here you must selected Usage = ‘4’ – Plant maintenance as shown in below screen shot.
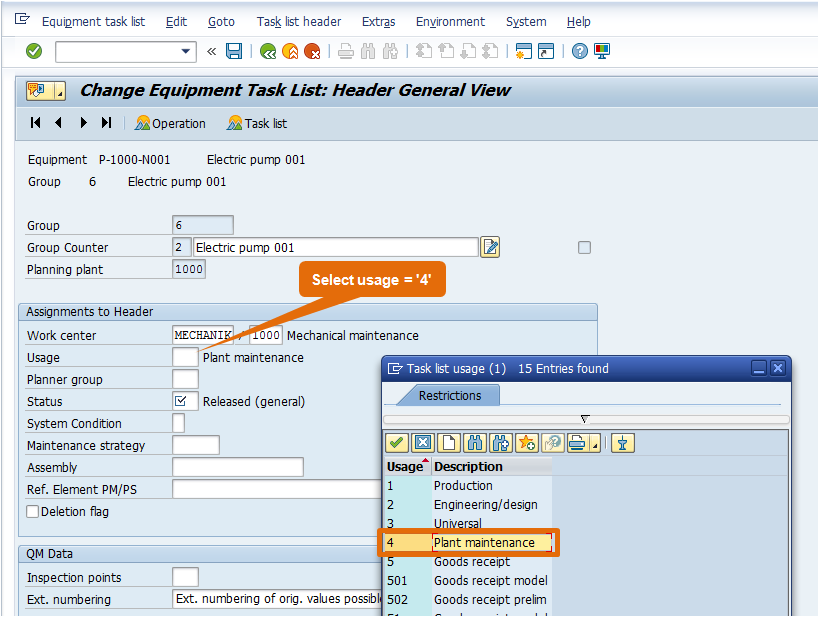
Step 4: Select Planner group from drop down.
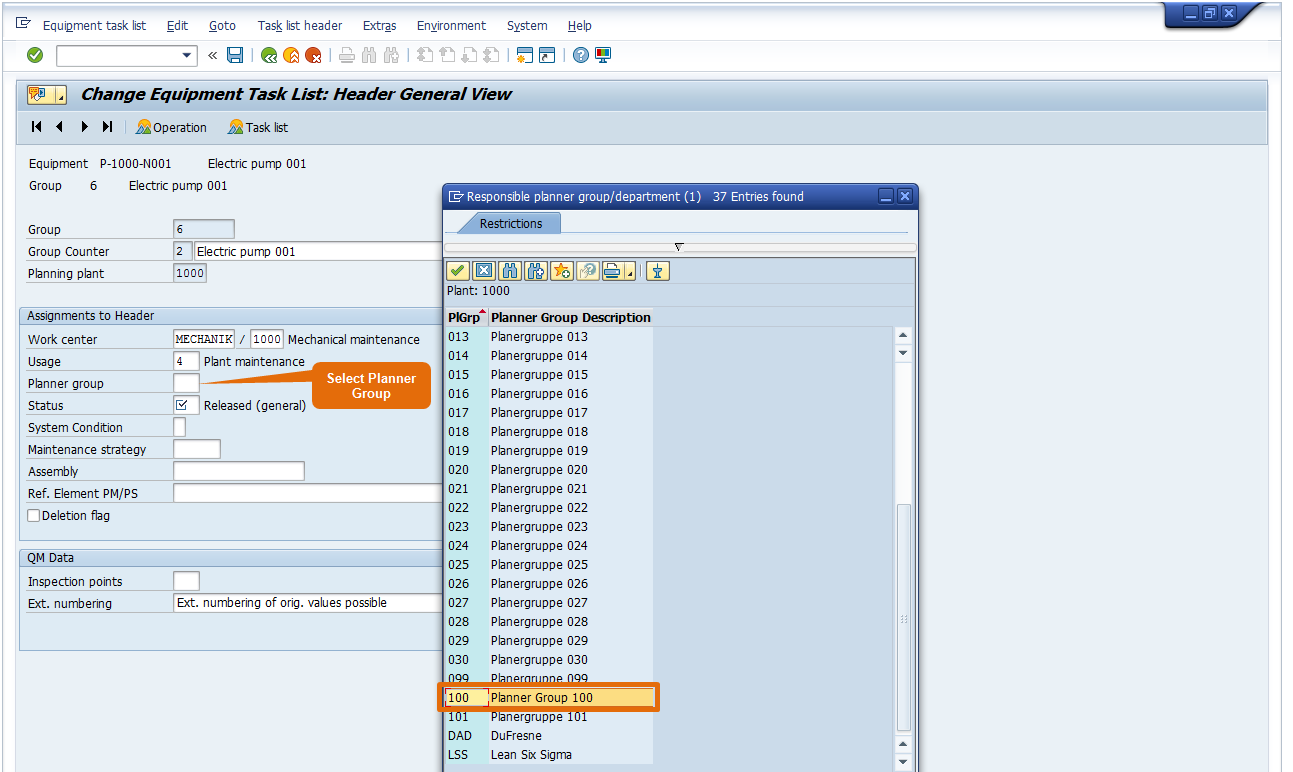
Step 5: Select Status = ‘4’ – Release (general)
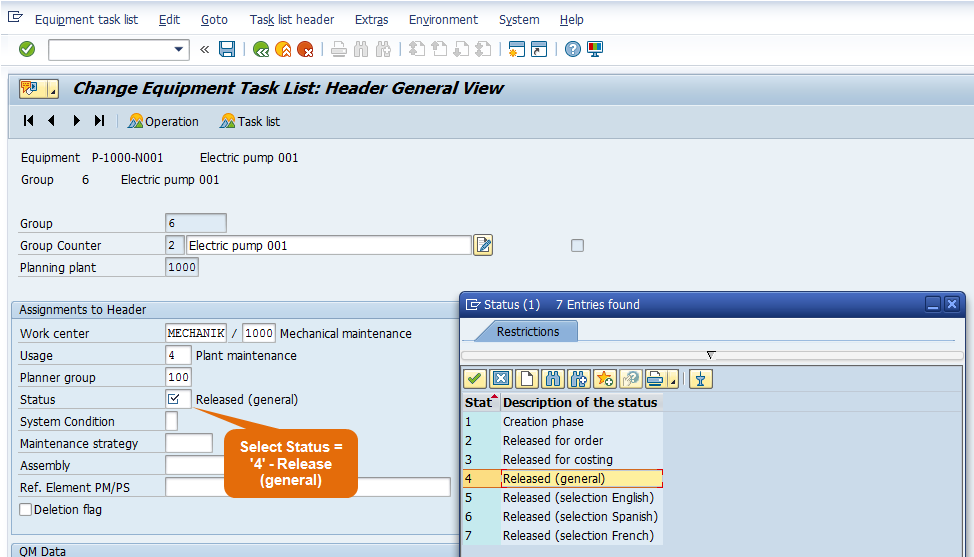
Step 6: Select System Condition. It shows the state of equipment during maintenance. Whether equipment will be in operation or not in operation when these maintenance operations will be performed.

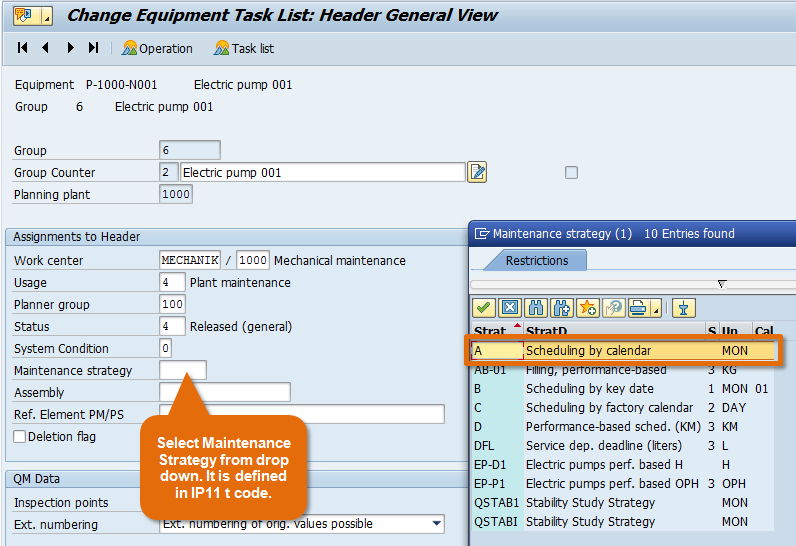
Step 7: Maintenance Strategy decides the cycle (frequency) of each maintenance operation. You can keep this field blank (for Single Cycle Plan) or select the maintenance strategy from drop down. Maintenance strategy is defined in t code IP11.
Step 8: Select Inspection Point = ‘300’ from drop down or else enter it directly. When you make an entry in this field, all sampling procedure data in the task list is used for inspection processing based on inspection points. It is used in Calibration Process. This is an integration between PM and QM Module.
If you carry out calibration inspections and want to record inspection results for equipment or functional locations, choose the inspection point type for Equipment or Functional location. You can create your own field combinations for these inspection types in Customizing. However, the field Equipment or Functional location must exist in the field combination.
if we fill field inspection point it will generate inspection lot even without mention inspection characteristic.

Step 9: Click on Operation Button at the top as shown in the below screen shot.

Step 10: See the below screen very carefully. It has very important information.

Main Work Center is copied from Task List header. Here you can see that it is maintained for each maintenance operation because it tells us who will execute the particular maintenance operation.
Control Key decides whether operation will be executed internally or externally. Means if an operation is executed by our own man power then we will select control key as PM01. However, if we want an external person or contractor to do the operation then we select control key as PM03.
Operation description give us clear cut information and sequence of maintenance activities to be performed on technical object.
‘Work’ (Man hours) is calculated as per formula :
Work = No. of persons X duration
No. of persons means the count of persons who are deployed to execute the maintenance operations.
Duration is the time taken by maintenance person to finish the task.
Calculation Key is the indicator which decides the formula to calculate Work. Sometimes client does not want to calculate man hours. They only want to calculate duration, then they select calculation key = ‘1’. But generally we recommend to calculate man hours using Calculation Key = ‘2’.
Activity Type is a very important function. It is copied automatically from Main Work Center data. It is defined by Controlling person. It contains the information of rate of man hours. When it is multiplied with Work (man hours), it give the cost of internal services. This helps in maintenance order costing. Do not confuse Activity type with Maintenance Activity Type. Both are entirely different.
Integration : Assignment of Activity Type in Task List and Maintenance order is an integration of PM module with CO module. CO person creates Activity type using t code KP26. Even a PM consultant can easily learn step by step process of creating Activity Type. We will include a separate article on this topic in near future.
Step 11: Assign components (spare parts) to the operations wherever applicable. For example: For cleaning and lubrication maintenance person can have requirement of Lubricant or maintenance person wants to replace the bearing of a machine. To capture such information first select the operation for which you want to issue material from warehouse. Then click on Component button at bottom (as shown in below screen shot).

Step 12: A new screen will appear where we can select the material (spare part) and enter quantity. We can also select the relevant Item Category.
If item category is ‘L‘, then material will be issues from warehouse through reservation.
If item category is ‘N‘, then material will be procured through procurement cycle (PR -> PO -> GR).

Step 13: If you want to execute a certain maintenance operation by an external agency (Contractor), then you must select the control key PM03. By using control key PM03, you can assign services from service master, quantity and gross price. This helps in calculating the cost of externally procured services in maintenance order.

Step 14: Once you click on Service Package button it will open a new screen where you can enter the service master with quantity.

Step 15:Click on back button and SAVE button. This will save equipment task list.
The post Equipment Task List in SAP PM appeared first on VaibhavERP.
I have discussed about equipment task list and functional location task list in my earlier posts. Lets have a look on General Task List in SAP PM. It is also a part of Master Data in SAP PM.
General Task List is not an Object based task list because it is not created with reference to a technical object. In SAP we use indicator ‘A‘ to identify general task list. T code to create a General task list is IA05.
General Task List is widely used in the preventive maintenance and routine maintenance. It is comprises of maintenance operations which are common to several technical objects (Equipment and functional location both). of critical and unique equipment, which requires some special maintenance operations to be performed at scheduled intervals. Suppose a maintenance work is to be performed on an equipment and maintenance tasks are specific (not general) to that equipment. In such a situation, we use equipment task list.
Step 1: Run t code IA05 or go to node on SAP Easy Access Screen as shown in the below screen shot.
Step 2: Enter the Task List Group number. You can enter the group name externally or else system will generate a new number internally . Then press enter or click on tick mark as shown in below screen shot.

Step 3: Planning Plant and Main Work Center will be entered manually. Group Counter will automatically update from system or else you can update it externally. Group is also updated internally from system. Here you must selected Usage = ‘4’ – Plant maintenance as shown in below screen shot.
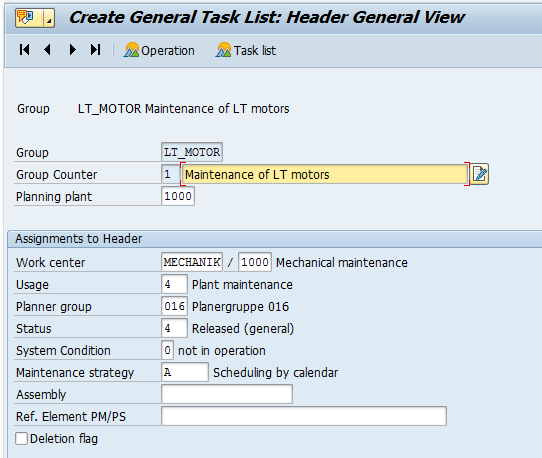
Rest all the entries are same as in Equipment Task List and Functional Location Task List. I request you to please refer my article on both topics.
The post General Task List in SAP PM appeared first on VaibhavERP.
Catalog is master data in sap pm module which is used to record technical information in a notification about the malfunction. It is used in maintenance processes to capture information related to maintenance history in the form of codes. Each code has a short description and a long description to showcase details of maintenance event. We can store catalog groups, codes and their respective descriptions in a Catalog.
While entering the maintenance history we can use these catalog codes in maintenance notification and measuring points and measuring documents. Business benefit of using catalog codes is the data redundancy. Business user is not required to enter same history description again and again. They can simply use the code.
For example:
If user wants to enter “Leakage in Pipe”. Then user can simply enter the code such as “0001” or “LKGP” or “MEC1”. User is not required to enter the entire text every time when any leakage happens. We will have to maintain all such codes in SAP while configuring the system.
We can create catalog codes with reference to catalog. Catalog can be Cause, Damage, Object etc.
Group of all such codes is known as Catalog in SAP PM. We also recommend to go through the article on concept of catalog profile.
Let us understand the step by step process to create a catalog and code in SAP PM.
Step 1: Run t code QS41 or go to this path
Logistics->Plant Maintenance->Maintenance Processing->Environment->Catalog->Edit

Here you will get a selection screen

Where you can select the relevant Catalog such as 5 – Cause, C – Damage or B – Object part.

Press enter and get into the Code Group overview screen
Step 2: As per the screen shot below enter description, status and go to code section.

Step 3: Click on New Entries button as shown in the screen shot below.

Step 4: Enter code and short text for code. This information is the maintenance history which will be used again and again in maintenance notifications.

Enter short description of code. Maximum length is 40 characters.
Step 5: Click on SAVE button.

Once you click on SAVE button, system will ask you to create a transport request as shown in below screen shot.
Enter the short text and click o SAVE button.
Usage of Catalog and codes will be explained in maintenance notification processing.
The post Catalog in SAP PM appeared first on VaibhavERP.